How To Calculate Matrix Size In Ct
SNR is directly proportional to voxel size assuming that the number of phase encoding steps is held constant. B Matrix size is 215 215.
A Matrix size is 64 64.

How to calculate matrix size in ct. 0313 mm for 1024 1024. The depth the pixel represents is determined by the slice thickness. First calculate the dimension divde dfov x matrix then square the answer how do you calculate the smallest object able to view if the limiting resolution is 15 lpcm first take the number and make it reciprical.
Substantial contributions are the properties of the CT device namely the X-ray source focal spot size and the detector pixel size scattering but also the used magnification in cone-beam geometry. As for matrix size 512 512 has been used in conventional CT but larger matrix sizes such as 1024 1024 and 2048 2048 are available with U-HRCT. MATRIX CT Image is represented by a matrix of numbers Rows and Columns of pixels Slide 38 Rows and Columns of pixels 512 X 512 Matrix 262144 Pixels 256 340 512 768 1024 80 160 180 not used today THE IMAGE IS MADE OF BLOCKS Slide 39 MATRIX The bigger the matrix the smaller the pixel size reduces partial volume i Slide 40.
Reducing the FOV increasing the matrix number or reducing the slice thickness results in an image with reduced voxel volume. Frequency256 Phase192 FOV200 200256 Frequency direction 200192Phase. If your transformer has a voltage ratio is 125 means the CT ratio would be 251.
C Matrix size is 1024 1024. Increased voxel size results in an increased signal-to-noise ratio. Most of the phantoms are suitable for micro CT measurement with voxel size above s μm and object size in the order of centimeters.
A CT image is composed of a square image matrix that ranges in size from 256 X 256 to 1024 X 1024 picture elements or pixels. How to calculate Pixel Size. Increasing the number of smaller pixels will improve the quality of the image.
SNR is directly proportional to voxel size assuming that the number of phase-encoding steps is. V p V s I s I P 2. Because for every line there is a space.
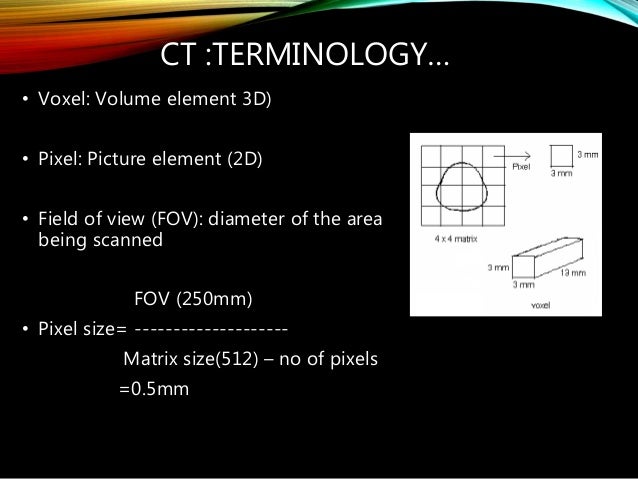
It means if the CT has a primary current of 25 Amps you get 1. The size of this voxel depends on the matrix size the selected field of view FOV and the section thickness. Pixel Size The pixel size can be calculated by dividing the DFOV in mm by 512 the matrix.
Pixel size is typically between 05 and 15 mm. CT numbers above the range are displayed as white and CT numbers below the range are displayed as black. Since a CT section has a finite thickness each pixel actually represents a small volume element or voxel.
We can calculate the size of our pixel by taking the field of view FOV and dividing it by the frequencyphase value. The CT ratio is the inverse of the voltage ratio. The matrix size is typically 128x 256x or 512x.
The pixel size FOVmatrix determines the in-plane resolution. Orient1 vectorImageOrientationPatient0 ImageOrientationPatient1 ImageOrientationPatient2 orient2 vectorImageOrientationPatient3 ImageOrientationPatient4 ImageOrientationPatient5 orient3 orient1 x orient2 cross product orient_matrix matrixorient1 orient2 orient3 pos1 vectorImagePositionPatient0 ImagePositionPatient1. Size FOVmatrix determines the in-plane resolution.
FIGURE 2-2 For a given field of view the larger the matrix size the greater the number of smaller individual pixels. The trade-off for increased voxel size is decreased spatial resolution. The typical CT image is composed of 512 rows each of 512 pixels ie a square matrix of 512 x 512 262144 pixels one for each voxel.
Determines the range of CT numbers displayed by the gray scale. Small voxels produce MR images with high spa-. The depth the pixel represents is determined by the slice thickness.
The smaller the pixel size the greater the image spatial resolution. CT numbers above the range are displayed as white and CT numbers below the range are displayed as black. In conclusion a measurement made by a detector CT is proportional to the sum of the attenuation coefficients.
The spatial resolution of a CT measurement is affected by a multitude of factors. Look at the formula 1 and 2. Calculated by dividing the DFOV in mm by 512 the matrix.
Multiply phase pixel size by frequency pixel size pixel area squared Frequency dimension of a pixel FOV frequency matrix. This will then be cut in half. The pixel size is equal to the field of view divided by the matrix size.
And 0156 mm for 2048 2048 Fig 1. When the reconstruction of the field of view FOV is set to 320 mm to cover the entire lung the theoretical size of 1 pixel in an image matrix is 0625 mm for 512 512. Reducing the FOV increasing the matrix number or reducing the slice thickness results in an image with reduced voxel volume.
Manufacturing and reference measurement of calibration object for CT with the small field of view under 1 mm is a challenging task. 15lpcm to 115 then to 1015. Divide 15 in to 10 06.
Pixel size FOVfrequencyphase value Example. 03 is the answer. CT measurement such as voxel size and edge detection calibration 22 23.
The measurement strategy especially the number of.

Pin On J Make Gold Diamonds Daily
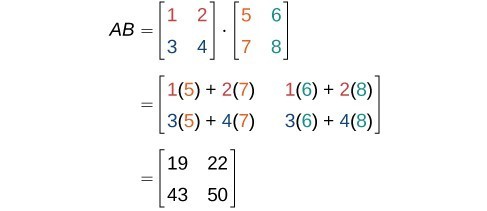
Finding The Product Of Two Matrices College Algebra
X Ray Image Formation And Contrast

How To Solve Matrix Using A Calculator Youtube
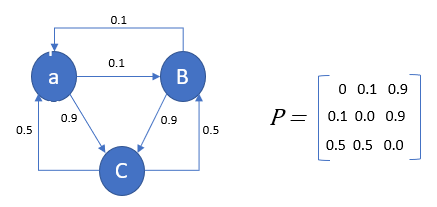
Markov Chain Analysis And Simulation Using Python By Herman Scheepers Towards Data Science
Computed Tomography Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Ct Numbers Window Width And Window Level

How To Calculate Time Complexity Of Your Code Or Algorithm Big O 1 O N O N 2 O N 3 Youtube

Ct Image Quality Frcr Physics Notes

Mathematics Finding Rank Of Matrix Youtube








