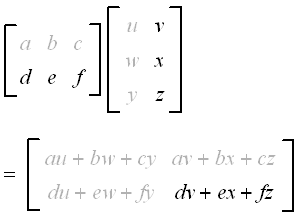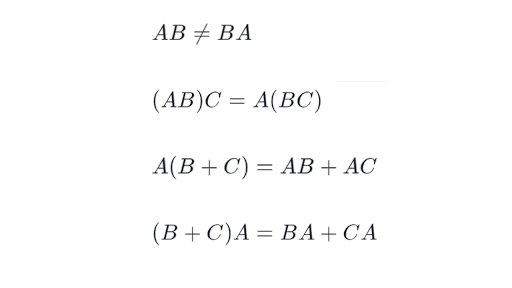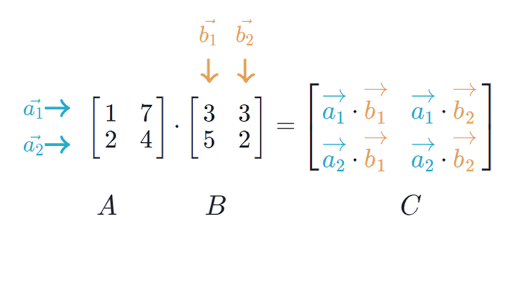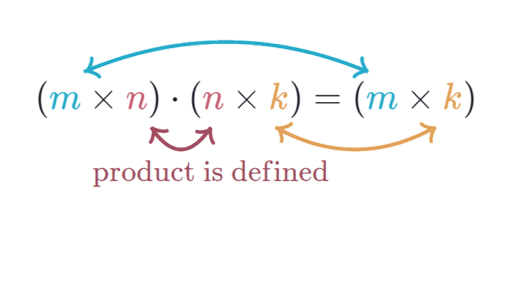Matrix Multiplication Dimensions Rules
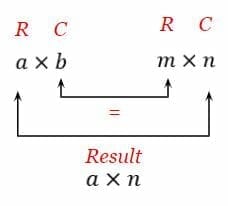
Then all you do is iterate over rows of A i and columns of B j and the common dimension of both k matlaboctave example. If the first matrix has a dimension of a times b and the second matrixs dimension is m times n for matrix multiplication to be defined the number of columns of the first matrix b must equal the number of rows of the second matrix m.
The dimensions of the matrix will remain the same before and after the multiplication.

Matrix multiplication dimensions rules. The integer will be distributed to each entry in the matrix by multiplication. Say you have A mn and B np. So first lets look how matrix multiplication works.
If A is not square then A A doesnt work for matrix multiplication. Multiply the elements of each row of the first matrix by the elements of each column in the second matrix. A matrix with 2 columns can be multiplied by any matrix with 2 rows.
Matrix Multiplication Defined page 2 of 3 Just as with adding matrices the sizes of the matrices matter when we are multiplying. A B c i j where c i j a i 1 b 1 j a i 2 b 2 j. Suppose we have two matrices A and B of dimensions 23 and 32 respectively.
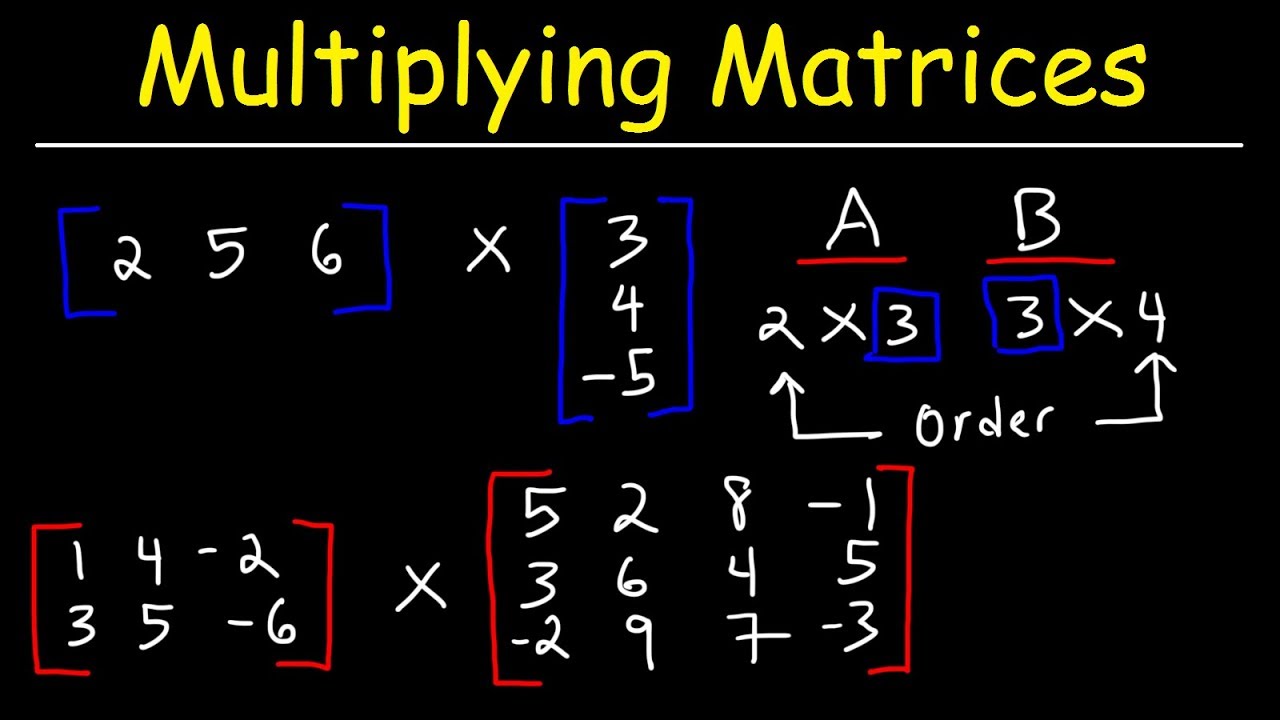
The rule for matrix multiplication however is that two matrices can be multiplied only when the number of columns in the first equals the number of rows in the second that is the inner dimensions are the same n for an m n-matrix times an n p-matrix resulting in an m p-matrix. As a result of multiplication you will get a new matrix that has the same quantity of rows as the 1st one has and the. For matrix multiplication to work the columns of the second matrix have to have the same number of entries as do the rows of the first matrix.
One requirement is that number of columns of A must match the number of rows of B. The resultant matrix will have dimensions a times n. Multiplying each element in the matrix by the integer will produce the answer matrix.
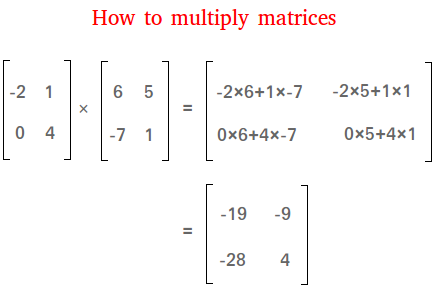
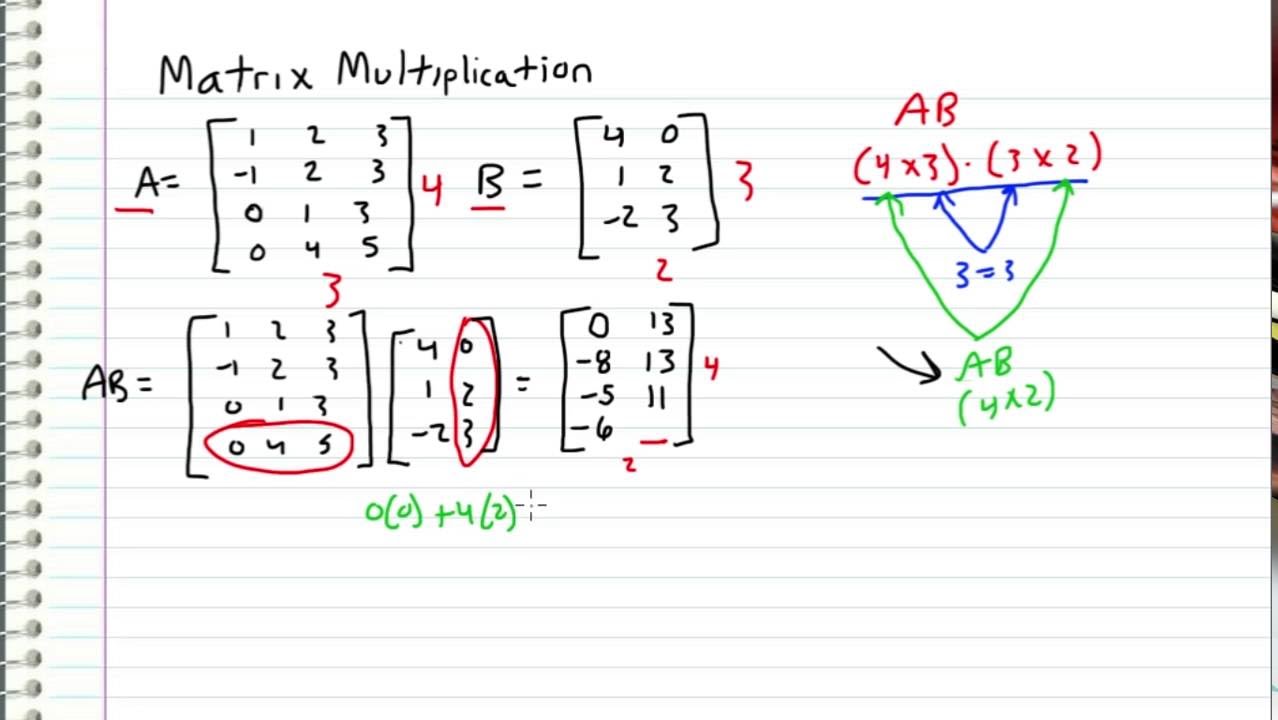
To find the first element of the resultant matrix multiply the first row of matrix A by the first column of matrix B and sum up the product. If A a i j is an m n matrix and B b i j is an n p matrix the product A B is an m p matrix. Make sure that the the number of columns in the 1 st one equals the number of rows in the 2 nd one.
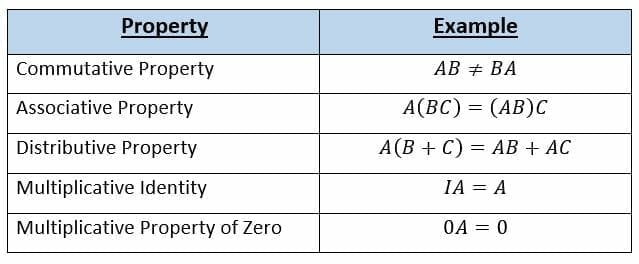
Let us say we are multiplying three matrices A B and C and the product is D ABC. If A is a square matrix then A A is well-defined. When you multiply a matrix by a integer it is called scaler multiplication.
The matrix multiplication operator calculates the product of. About the method The main condition of matrix multiplication is that the number of columns of the 1st matrix must equal to the number of rows of the 2nd one. These matrices may be multiplied by each other to.
The resultant matrix will be a 22 matrix. The dimension property states that multiplying a scalar with a matrix call it A will give another matrix that has the same dimensions as A. The pre-requisite to be able to multiply Step 2.
Multiplication of the three matrices will be composed of two 2-matrix multiplication operations and each of the two operations will follow the same rules as discussed in the previous section. The usual rules for exponents namely P and AP still apply. Here are the steps for each entry.
That is the number of columns in the first input must be equal to the number of rows in the second input. 2 x 3 times 3 x 3. You can only multiply two matrices if their dimensions are compatible which means the number of columns in the first matrix is the same as the number of rows in the second matrix.
An easy way to determine this is to write out each matrixs rows x columns and if the numbers on the inside are the same they can be multiplied. But if you use the matrix multiplication operator to multiply two matrices then the matrices must have a common inner dimension. In order to multiply matrices Step 1.
24 28 22 48 4 32 36. These properties include the dimension property for scalar multiplication associative property and distributive property. A i n b n j.
We can use this information to find every entry of matrix C. 3 Matrix Powers We can take powers of matrices but only if theyre square. Now the rules for matrix multiplication say that entry ij of matrix C is the dot product of row i in matrix A and column j in matrix B.
We define A I where I is the identity matrix of the same size. In this lesson we will look at the properties of matrix scalar multiplication.
Matrix Multiplication Dimensions Article Khan Academy
Matrix Multiplication Made Easy
Matrix Multiplication Calculator
Properties Of Matrix Multiplication Article Khan Academy
Linear Algebra 4 Matrix Multiplication Youtube

3 4a Matrix Operations Finite Math

How To Multiply Matrices Quick Easy Youtube
Multiplying Matrices Article Matrices Khan Academy
Matrix Multiplication Dimensions Article Khan Academy
Matrix Multiplication Made Easy

A Complete Beginners Guide To Matrix Multiplication For Data Science With Python Numpy By Chris The Data Guy Towards Data Science
Matrix Multiplication Explanation Examples
Matrix Multiplication Explanation Examples
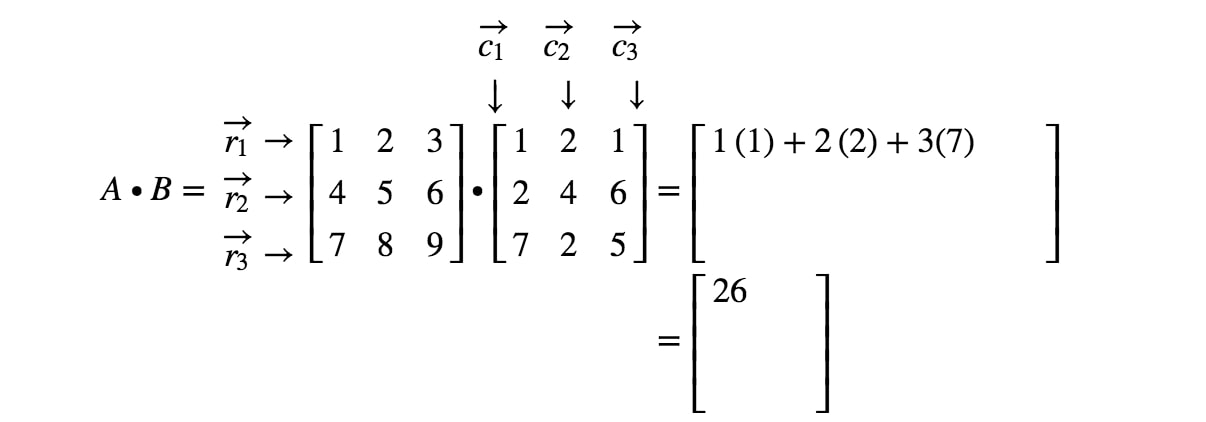
How To Multiply Two Matrices Together Studypug